Blooming Skin Within: A Holistic Approach to Beautiful, Healthy Skin

When I started my skin clinic, I had a vision to help people achieve healthy, radiant skin by focusing on their inner well-being. My skin ethos is grounded in science, knowledge, and testing, which has only grown stronger through collaborations with doctors, scientists, and fellow skin practitioners. Together, we’ve confirmed that true skin glow starts at the cellular level.
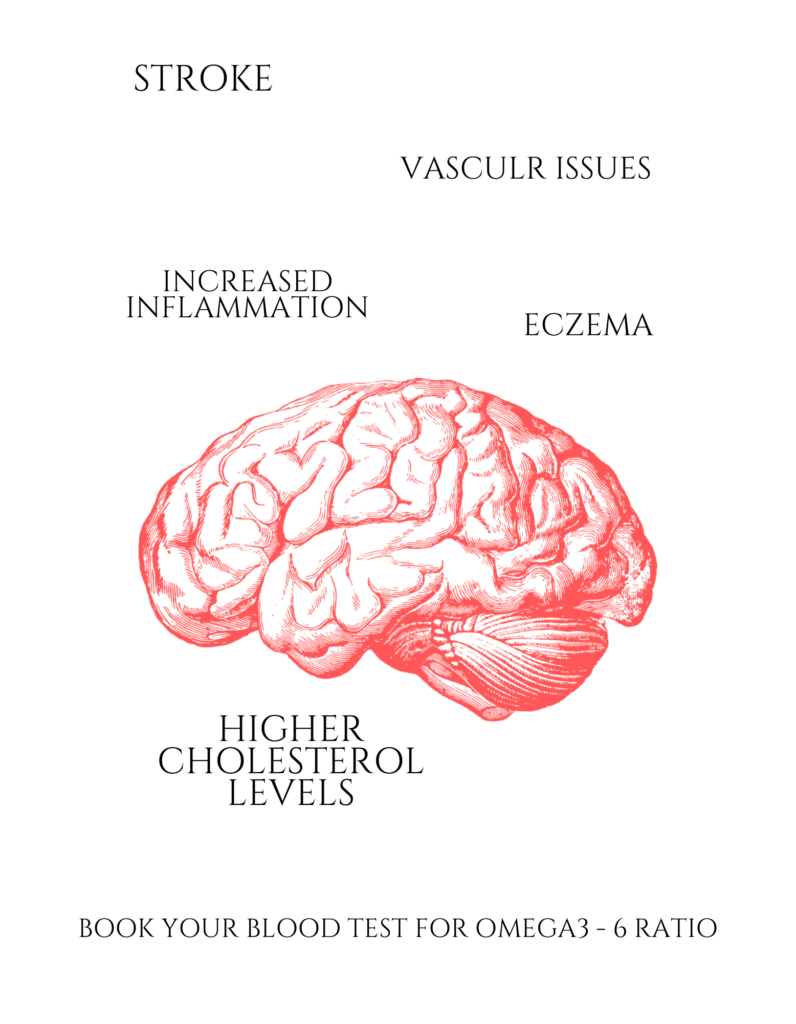
A few years ago, I introduced a nutrition-based blood test to my clinic, which measures 11 essential fatty acids crucial for overall health. Many clients assume they’re balanced because they eat healthily, but I always encourage, “DON’T GUESS– TEST!” Essential fatty acids are vital components of our cells, essential for brain, heart, nails, hair, and skin health. An imbalance can lead to various issues like cardiovascular problems, skin conditions, and more.
The blood test is scientifically proven to help you make informed dietary changes for optimal health. My philosophy is simple: healthy cells lead to glowing skin. Let’s work together to achieve your skin goals and prioritize your health in 2025. Book your essential fatty acid blood test now, and let’s unlock your skin’s full potential. Your health is in your hands!
Test accuracy and reliability: The essential fatty acid blood test is based on sound scientific research and is a reliable tool for assessing your nutritional status.
Easy and convenient process: The testing process is simple and convenient, ensuring a hassle-free experience for you (finger prick blood test)
Expert guidance: I will help You interpret your test results and develop personalized strategies to optimize your essential fatty acid balance, which ultimately improves your overall skin health and appearance.
Transformative results – True Story: I struggled with severe melasma, leaving my skin looking patchy and dark. Additionally, I felt unwell overall. Desperate for a solution, I turned to Karolina for help. She recommended a health protocol that included a blood test and natural health supplements, which have been life-changing for me. After just one month of following her advice and taking the recommended supplements, my skin began to brighten, and I felt stronger and more energized. The brain fog I had experienced before dissipated, and my skin looked noticeably healthier – even my coworkers took notice! I’m thrilled with the progress I’ve made so far and cannot recommend Karolina’s expertise highly enough. If you’re seeking a skin expert who takes a holistic approach and delivers real results, look no further than Karolina.
ADVANCED SKIN SPECIALIST – KAROLINA